This is an interesting problem that we’re going to talk about today. I’m currently
working on adding framebuffer support in RTEMS Beaglebone black and the
approach I have selected for doing the project is to use code from FreeBSD and
port it to RTEMS, so, basically I’m importing the am335x_lcd driver and the
tda19988 driver from the FreeBSD in rtems-libbsd and the plan is to port the
FreeBSD driver to RTEMS. But the issue with this approach is that, the drivers
imported from freebsd uses the iicbus interface in the FreeBSD, on the other
hand RTEMS has it’s own well supported I2C stack that the RTEMS applications
use. We can, of course, choose to just replace the RTEMS I2C with the FreeBSD
iicbus stack but that will potentially break every application that used
the RTEMS I2C driver.
So how to address this then? The answer is to add an adaptation layer on top of the rtems driver, and connect it to the FreeBSD API.
The I2C Adaptation layer for libbsd
This is a very interesting situation and hence needs some interesting solution.
So we’re going to approach this problem by connecting the iicbus interface of
FreeBSD with the RTEMS I2C interface by introducing an i2c-adaptation layer in
between. So basically what we’re doing is letting the RTEMS driver deal with the
hardware, and on top of it, we’re accessing the created I2C device as an
application layer to RTEMS and connecting it with the FreeBSD API by acting as a
driver to the FreeBSD interface.
The Figure below shows the approach clearly.
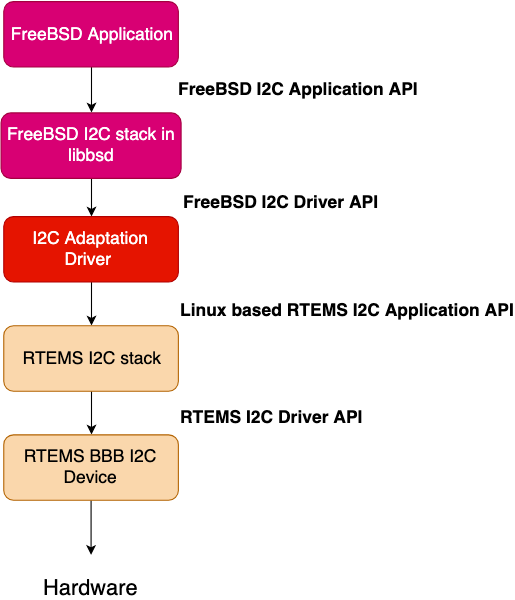
As we follow from bottom up. First we have the RTEMS I2C stack that uses the RTEMS Driver API to work with the BBB I2C device. This RTEMS driver is dealing with the hardware and all the hardware control is done by this RTEMS I2C stack. On top of it we’ve added another layer that we’re calling as the I2C adaptation layer.
From the adaptation layer, we’re using the FreeBSD Driver API and calling the ioctl on the RTEMS I2C stack as an application. This enables our lcd drivers, which will be FreeBSD application, to used the RTEMS I2C stack instead of the FreeBSD stack without having to alter any program flow in the FreeBSD drivers or breaking the whole I2C stack used by the RTEMS applications.
The Adaptation layer is nearly complete and I hope to merge it to the main repo soon. Since it doesn’t touch any other application part, it can be merged separately, independent of the rest of the Framebuffer work.
Hope You have found this article interesting. I would really appreciate if you’d like to add any ideas or approaches used in some other projects, and start a discussion below.
UPDATE : The I2C adaptation driver is complete and has been merged in the RTEMS Upstream repo. the commit link
Thank You for stopping by!

 RTEMS GSoC 2019 Project Introduction: Add Framebuffer driver for Beaglebone Black
RTEMS GSoC 2019 Project Introduction: Add Framebuffer driver for Beaglebone Black